What are the main components in a photovoltaic solar system?
- By user

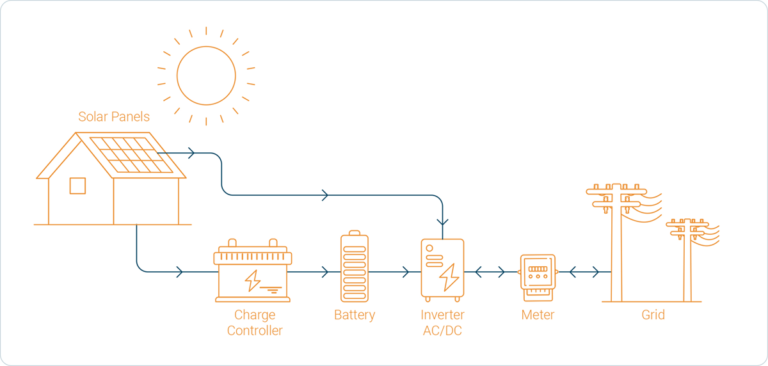
Grid-interactive solar PV systems generally consist of six individual components: the solar PV array, a charge controller, a battery bank, an inverter, a utility meter, and an electric grid. However, a charge controller and battery bank are optional. Even though these two components help you store and, as such, make better use of your generated solar energy, they also increase the total price of the installation.
Solar PV array
A solar PV array consists of a number of solar PV panels that are connected. The solar PV array generates DC electricity from sunlight. It is important to keep in mind that photovoltaic systems must be installed on stable mounting structures that can support the array and withstand weather conditions like wind, rain, and corrosion .
Solar PV panels or arrays are mounted on roofs with a mounting system using various railings, frames and tiles or tin feet. Most mounting systems are made of aluminium with stainless steel hardware and are designed to accept a variety of solar modules on different roof types
Superior mounting systems are manufactured with higher grades of aluminium and stainless steel, often resulting in less roof weight and lower levels of corrosion over a longer period of time. Quality mounting rails may also feature robust anchoring points and design solutions that speed-up the installation time of your solar system. Purchasing a strong and well-engineered mounting system is the sensible way to protect the investment you have made in your solar system
In addition the balance of system, consisting of cables, switchboards, junction boxes, meters, earthing system, circuit breaker, fuses etc. is required. These are minor hardware expenses, but they comprise a big chunk of the labour when you’re installing a PV system. It is recommended to use high quality materials and that you insist on high-quality workmanship.
Charge controller
Charge controllers regulate the DC electricity from the solar panels to prevent the batteries from overcharging. Charge controllers can be divided into two types: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) and Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). The PWM is a standard type and is suitable for smaller photovoltaic systems and battery banks. MPPT charge controllers are more suitable for larger systems. You only need a charge controller if you have a battery bank.
Battery bank
A battery bank helps you maximise your self-consumption of solar energy and it also provides you with a reliable back-up solution in case of grid outages. It stores the energy that is being produced by the PV array and is not consumed immediately. Including a battery bank in your solar PV systems is optional.
Solar inverter
A solar inverter is one of the most important elements of the solar electric power system and it is advised to get a good quality inverter. It converts the variable direct current (DC) output of a solar PV panel into an alternating current (AC). This AC electricity can be fed into your home to operate your household appliances. Depending on how your system is set-up the electricity that is not used in your home is either fed into the grid via electrical power lines or stored in batteries for later use.
Bi-directional energy meter
Regardless of your solar PV system, every building will have a service connection point with an energy meter to record the electricity consumption. The solar energy that you have generated from the solar PV system and that is not stored or self-consumed will be fed back into the public electricity grid. Bi-directional meters keep track of (i) the electricity drawn from the public grid and (ii) the surplus solar energy that is exported to the public grid.
Electric grid
Although solar PV is making off-grid electricity sourcing possible, most homeowners, and organization opt for a combination of solar PV- and grid-based electricity sourcing. If your building is connected to the public grid, the extra power that is generated from your solar PV system, once your battery bank is full, will be sent to the grid. This also means that during periods (night-time or cloudy days etc.) when the solar PV system doesn’t cover your energy needs, you will be able to supply your home with electricity from the grid. Depending on which state you are in the exported solar energy will attract monetary compensation either through a net metering, net feed-in or gross feed-in accounting mechanism.
Benefits of a solar PV system
The solar PV system can be designed for a variety of applications and can be adapted to your requirements and objectives. The system can be seized to optimize your financial returns or to meet your environmental targets.
Once properly installed, the system requires minimal maintenance.
It provides you with clean energy and the operation does not create any noise or pollution.
A solar PV system is modular, it is easy to expand or, even, in some cases, transport it.
It will reduce your electricity bill, as running the system is free.
The system is expected to have a lifetime of 20 to 25 years.
