How Solar Energy Can Transform Indian Industries
For energy-intensive industries, using solar energy can put them on the path to reducing their CO2 emissions. For the industry, it is both an environmental responsibility but also a step in reducing energy costs and gaining a competitive advantage. International carbon levies such as the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) are fast approaching, imposing additional costs on export-oriented goods and services. For industries that rely heavily on fossil fuels, sustainable solutions such as rooftop solar can transform both environmental impact and business viability.
Many industries are energy-intensive, with energy consumption being a major driver of their carbon footprint. This is particularly true for sectors such as:
- Steel: The steel industry is among the top emitters amongst the Indian industries, accounting for 12% of the country’s emissions. With the majority of processes needing energy to operate machinery or for heating, reducing energy emissions is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in the global market.
- Automobiles: This manufacturing sector contributes 16% of India’s CO2 emissions. Energy-intensive manufacturing processes, including steelmaking, casting, and assembly, contribute to nearly half of the automobile industry’s emissions.
- Cement: India is the second-largest polluter from cement manufacturing across the globe. This sector contributes nearly 8% to global emissions, and accounts for about 6% of India’s emissions. The most energy-intensive processes to make cement are responsible for approximately 30% of the industry’s total emissions.
- Textiles and Apparel: The Indian textile sector accounts for 6-8% of national GHG emissions. Energy-intensive processes like dyeing, spinning, and weaving can account for approximately 55% of the industry’s emissions.
- Chemicals: Production of chemicals, and chemical processes account for more than 4% of India’s emissions. Energy-intensive activities such as distillation, separation, and chemical synthesis drive a substantial portion of the chemical industry’s emissions, around 40%.
- Food and Beverage: This sector emits almost 2% % of India’s GHGs. Refrigeration, processing, and packaging are energy intensive processes that contribute significantly to the sector’s emissions, estimated to account for roughly 30% of its total emissions.
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
Figure 1: CBAM timeline.

From 2026 to 2034 few other industrial sectors will also be included under CBAM. In parallel, countries outside the EU are also developing similar mechanisms applicable to exports to their countries, notably the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, and a few others. Reducing emissions is not only an environmental imperative but also a strategic necessity to maintain competitiveness in the global market.
The steel industry is among the first sectors identified by the European Union (EU) that will be subject to the CBAM taxation starting from the 1st of January 2026. This means that steel products imported into the EU will be subject to additional tax based on the emission from the process, making it crucial for Indian steel producers to reduce their carbon emissions. For steel producers where detailed emission calculations are not readily available, a default emissions factor will be applied. This could potentially lead to a cost increase of up to 6% for imported steel products.
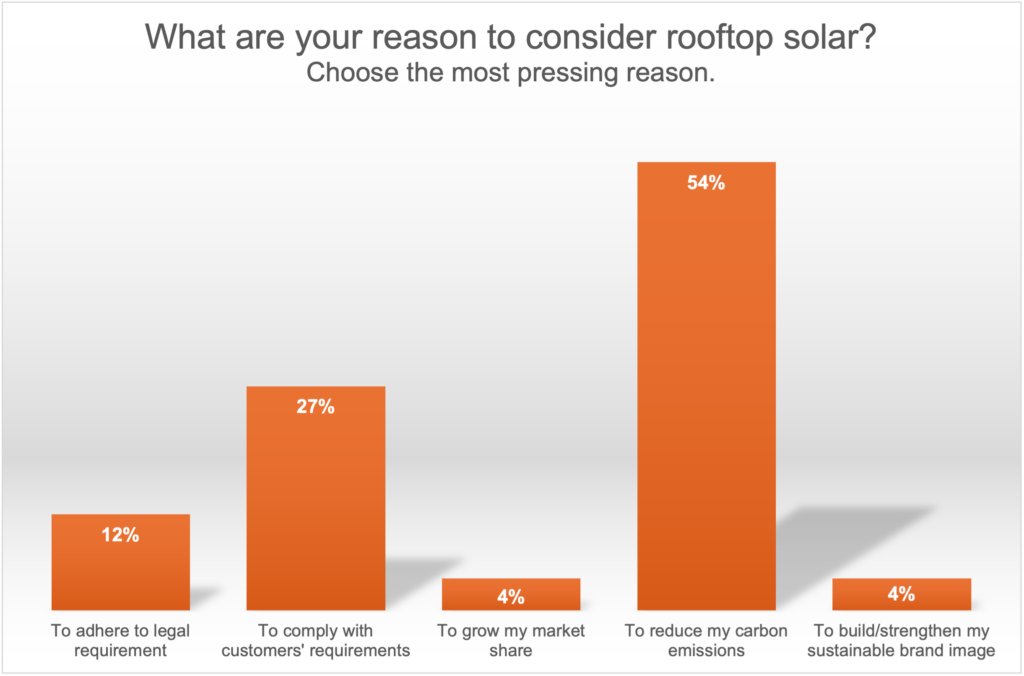
In a recent webinar we co-hosted, when we asked participants about their top reason for considering solar, the overwhelming majority selected to reduce carbon emissions
Figure 2: Poll results of webinar participants for considering rooftop solar as clean source of energy.
The Solar Solution
Rooftop solar offers a compelling solution for Indian industries to address rising energy costs, enhance energy independence, and reduce their carbon footprint.
- Maintain a competitive edge: Complying with regulations and reducing the carbon footprint directly influence import costs for buyers.
- Reduce energy costs: Significantly lower electricity bills, particularly for energy-intensive processes.
- Enhance energy independence: Minimize reliance on the grid, mitigating the risk of power outages and price fluctuations.
- Comply with national and international climate regulations: Meet stricter environmental regulations and avoid potential penalties.
- Improve sustainability: Enhance brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers and investors.
As India accelerates its transition to a low-carbon economy, supportive government policies, financial incentives, and technological advancements are creating a favorable environment for rooftop solar adoption. By embracing this clean and sustainable energy solution, Indian industries can not only reduce their environmental impact but also gain a competitive edge in the global market.
Get Started
(i) Know your supply chain and emissions. Use free tools, sector-specific tools, or reach out to greenhouse gases’ management consultants.
(ii) Identify opportunities to be more energy efficient. Switch to renewable energy sources
(iiI) Become energy-independent with RTS and energy storage solutions.
