The Sun’s Energy is Democratic: Rooftop Solar as a Solution for Domestic Consumers
- By user

Has your electricity bill increased significantly in the last year? Consumers are experiencing an accelerated increase in tariffs while energy providers face financial constraints of their own. By leveraging solar energy, households can significantly cut electricity bills, enhance comfort, and contribute to environmental sustainability. When combined with batteries, this solution can transform energy use in Indian homes. Are PM Suryaghar and other recent policy changes the shift we need to accelerate rooftop solar installations?
Domestic Energy Consumption
In India, the average household electricity consumption ranges between 3,600 kWh and 6,000 kWh annually, with the electricity tariff expected to increase year on year. A well-designed rooftop solar system can considerably reduce these expenses depending on local sunlight conditions and energy consumption patterns.
Combining solar panels with a battery energy storage system further enhances the potential of saving on electricity bills. Battery energy storage systems store excess energy generated during the day, which can be used at night, during cloudy periods and power outages. While power outages have a direct and noticeable impact in certain weathers, today we are dependent on electricity for more than just light and ventilation. By ensuring a reliable power supply, rooftop solar and battery energy storage systems can significantly improve daily comfort.
Mitigating Greenhouse Gas Emissions
India is grappling with an increase in tariffs, rising energy demands, frequent power cuts, and significant greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Rooftop solar offers a promising solution.
India’s electricity generation is predominantly fossil-fuel-based, leading to high levels of GHG emissions. According to 2024 estimates for each kWh of electricity produced approximately 0.72 kg of CO2 is emitted. Given that the average Indian household consumes around 3,600 kWh of electricity annually, this results in annual emissions of 2.55 tons of CO2.
Solar roofing offers a substantial reduction in these emissions. A 2 kW solar panel system would generate approximately 3,150 kWh annually resulting in an offset of approximately 2.24 tons of CO2, significantly reducing the billable units and carbon footprint associated with household energy consumption. By adopting solar technology, households not only lower their individual emissions but also contribute to India’s broader climate goals.
The necessity of public support and clear regulations
India has experienced a notable rise in rooftop solar installations compared to previous years. Public support and clear regulations are vital for accelerating this transition. Key areas where government intervention is needed include primarily financial support. Offering subsidies or low-interest loans can make solar installations more accessible to consumers. According to a study on the economics of rooftop solar adoption, financial incentives can make a significant difference in adoption rates by reducing the initial investment burden.
A recent notification regarding the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana rooftop subsidy scheme introduces provisions allowing consumers to include a battery energy storage system within their rooftop solar installations. Furthermore, it specifies that the capacity of hybrid inverters may align with the consumer’s maximum sanctioned load, even if the initially proposed rooftop solar system is of lower capacity. This enables consumers to expand their rooftop solar capacity up to the sanctioned load in the future. However, the subsidy will be applicable solely to the capacity of the rooftop solar PV system installed at the time of the application.
Secondly, regulatory clarity for installing solar panels and batteries is essential. This includes simplifying grid interconnection procedures and establishing technical standards for components (type of inverter, monitoring mechanism).
And thirdly, increasing awareness about the benefits of solar energy and available financial support can drive higher adoption rates. Educational campaigns can help homeowners understand the cost savings and environmental benefits of solar technology.
Maximising the benefits of making the switch
To fully capitalize on the benefits of solar energy, it is crucial to reduce electricity consumption. Switching to energy-efficient appliances is an option to reduce electricity consumption. Appliances now come with a star rating, allowing consumers to compare energy consumption of similar products. Air conditioning is a major energy consumer, and alternatives such as a 4 or 5 star AC will reduce this, by consciously choosing to use ceiling fans when the weather is pleasant. Additionally, investing in effective solar shading can significantly cut electricity use and increase long-term savings. The same applies to lights and other appliances that rely on electricity.
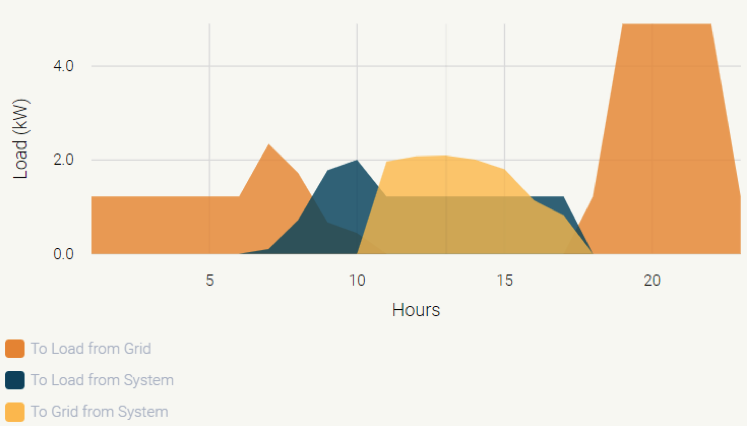
Switch to consuming solar-generated electricity when it’s most available – during the daytime. For example, you could run your washing machine during the day.
Conclusion
With policy changes from the central government, financing options, and increasing sanctions for rooftop solar, it is the right time to transition to more efficient equipment and adopt to rooftop solar.
Looking for more tips? Read our other blogs:
Navigating the Solar Buying Journey
About Suryaghar Muft Bijli Yojana
Find installers near you – enter your city and hit Search.
